Not Enough Agricultural Land This problem of agriculture is faced by people all over the world. This paper reviews the past trends the present and the future prospects facing the agricultural sector in general and the agribusiness industries in particular.

Food Security And Unsustainable Agriculture In Malaysia
Covid-19 a new strain of the coronavirus has posed challenges to all economic sectors especially agriculture.

. But in fact agriculture along with fisheries and forestry still accounts for 7-8 percent of Malaysias gross domestic product which is a high level for a country at Malaysias stage of economic development. They range from lack of access to modern farming equipment and technology high cost of fertilizers and pesticides high cost of labour land grabbing by developers and low prices for produce due to competition with imports. This is one of the leading issues that they are facing every day.
The sector also involves around one million workers with. On the manpower bit we just touched on employment in the agriculture sector has actually dropped slightly from 1570300 in 2018 to 1541100 persons in 2019. The World Bank took action to fight food insecurity around the world providing immediate aid to vulnerable.
The key challenges include the following. The decline was due to the commodity sub-sector especially oil palm which recorded a negative growth of 36 per cent 2019. Approximately 30 percent of the worlds population lacked access to adequate food in 2020 and into 2021.
With people staying indoors cooking at home has been on the rise. The Labor Sorrow It was all started about the tax that laborers are shouldering. There is a lack of up to date agricultural research and efficient use and unavailability of fertilizers and other farm outputs like quality seeds.
The swine sector is centralized and regulated by GOM to ensure the industry is free from disease outbreaks after the outbreak of Nipah virus in 1998. Major problems besetting the Agricultural and Agribusiness sector are identified. Deforestation and concrete jungles are taking up maximum area leaving little to no room for farming.
Competition for land for property development environmental pressure to limit deforestation increase price of acquiring new land for agricultural purposes. The reforms must focus on farmers livelihood improvement rural economic and infrastructure development food security and improving agro-based industries. Malaysia has a relatively strong agricultural research capability especially in the palm oil sector and the extension system is effective.
Inadequate physical infrastructure to support the sector Poor farming techniques Limited access to quality farm inputs Too much relying on rain. No significant beef industry exists. High cost of investmentfinance.
The National Agricultural Policies formulated for the benefits of the sector are also discussed in detail. Also on issues of food security and increasing the income level of the poor which is one of the National Key Result Area statisticsinformation on agriculture like SUA agricultural indicators salaries and wages labour force numbers imports and exports production data cost pattern etc. In Malaysia the Movement Control Order MCO 1 initially caused some panic buying.
One of the problems faced by the agricultural sector in Malaysia is the increasing cost of new land and development and scarcity of land due to more remunerative alternative uses. Like the previous year news in agriculture and food in 2021 was dominated by deteriorating food security. Agriculture industrial and domestic is still continuing in addition to lack of internal coordination and absence of agreement among the main users which calls for developing a vision for water policy.
A- The random usage of water in the three main sectors. The percentage growth of this sector declined 22 per cent from 20 per cent in the previous year. B- Weak participation of water users in its management.
The steady industrial growth coupled with the ever-increasing urbanization is leaving little to no room for any agricultural land. The significant cost of power or electricity that is shouldering by our farmers are a big problem. The cost is too expensive and sometimes lost half of the farmers profit.
Expanding agricultural land can also lead to deforestation additional GHG emissions and a loss of biodiversity. Additionally there are also the issues of the lack of ability to manage natural disasters and waste from inadequate farming practices. They have been scared by scammers who tell them to plant bananas lemongrass chili fertigation agarwood and teak only to fail technically or have no buyer once the crop is ready to harvest.
The challenges faced by farmers in Malaysia are many and varied. The purpose of the reforms should be the transformation of traditional agriculture to commercial agriculture to face global challenges. This affects the loss of perishable goods and also increases largely the costs associated with the production.
In addition irrigation of agricultural crops comprises 70 of global water use and agriculture directly contributes to around 11 of global greenhouse gas GHG emissions mostly through cattle. It does not even get much attention in the 10th Malaysia Plan 2011-2015. The contribution of the agriculture sector to Malaysias GDP in 2020 is 74 per cent.
Local Malaysian farmers have been indoctrinated by the agricultural backgrounds of their localities and that their land holds limited crop opportunities. Agricultural credit of over 50 billion per annum is not provided to the small farmer and nor does it fulfil the requirements. This has to be done with Private Sector participation.
Lack of marketing data and information Inadequate production and post harvest technologies. This has led to high demand for fresh food items at local markets and supermarkets. Are important inputs for strategic planning too.
Inadequate disease control facilities. Adding to the concerns is the Covid-19 pandemic that has severely affected all sectors of the economy including agriculture. One of the main issues in this regard is the lack of and the poor conditions of rural roads linking the farmers facilities and the commercialization spots in the country.

Malaysia Agriculture Forestry And Fishing Britannica

Australia A Trading Partner From Down Under

Economy Survey Resilient Agriculture Sector Growth At 3 9 In 2021 22 Business Standard News

Combatting Japan S Agricultural Worker Shortage

Top Solutions To The Problems Of Agriculture

Formulation And Manufacturing Process Of Production Of Pesticides Insecticides Fungicides Fungicide Insecticide Plant Problems

Agriculture And Economic Development Ipleaders
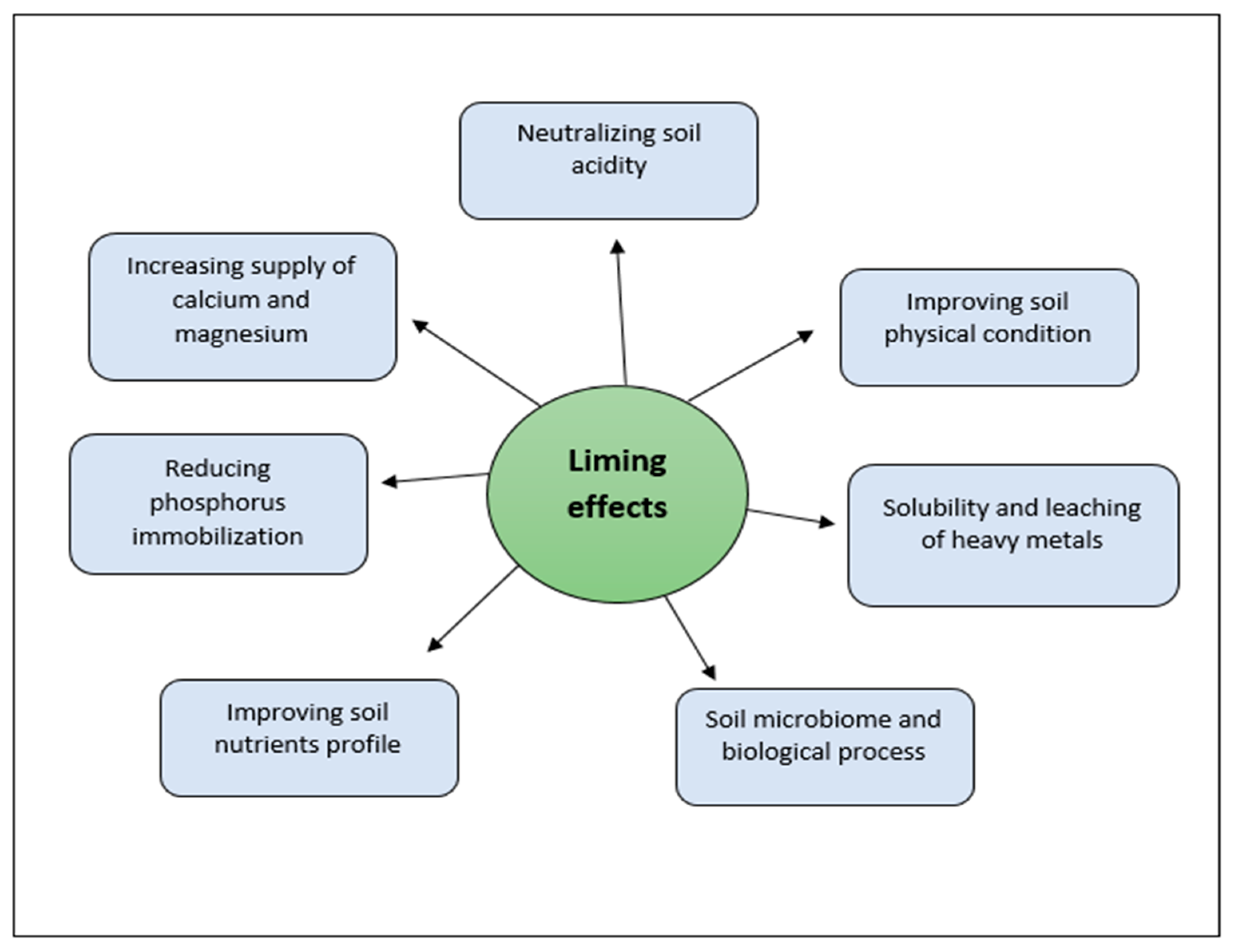
Agriculture Free Full Text Effects Of Liming On Soil Properties And Its Roles In Increasing The Productivity And Profitability Of The Oil Palm Industry In Malaysia Html

Agribusiness Can Lead The Shift To Sustainable Farming Bcg

High Value Crops Help Central Asia Revitalize Agriculture Sector Development Asia

Fasciola And Paramphistomum Infection In Large Ruminants Research Paper Agronomy Agricultural Science

Regenerative Agriculture Nestle Global

Transforming Agriculture In Asia Ado Update 2021 Theme Chapter Asian Development Bank

The Report Sri Lanka 2018 Infographic Indian Ocean Positivity

Green Nanotechnology For Sustainable Agriculture In Malaysia Fftc Agricultural Policy Platform Fftc Ap

Agriculture Food Supply Chain Scenario During The Covid 19 Pandemic In Malaysia Fftc Agricultural Policy Platform Fftc Ap

Gro S 2022 Watchlist 9 Major Themes For Agriculture In The Year Ahead

Transforming Agriculture In Asia Ado Update 2021 Theme Chapter Asian Development Bank

Growing Pains Southeast Asian Farmers Need Cheaper Agritech Agriculture Al Jazeera
